What is Mental Health: Understanding and Supporting Wellness
Understanding Mental Health conditions
Mental health is a state of well-being that enables people to cope with life’s stresses, realize their abilities, learn well, and work well.
Mental health is a basic human right and crucial for personal, community, and socio-economic development.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), mental health is a component of overall well-being and can influence and be influenced by physical health.
Mental health involves effective functioning in daily activities resulting in emotional well-being and contributing to community or society.
Types of Mental Health Conditions
Mental health conditions include mental disorders, psychosocial disabilities, and other mental states associated with significant distress or impairment.
Examples of mental health conditions include depression, anxiety disorders, schizophrenia, eating disorders, and addictive behaviors.
Bipolar disorder is a type of mental health condition that affects mood, thinking, and behavior.
Anxiety disorders are the most common mental health disorders.
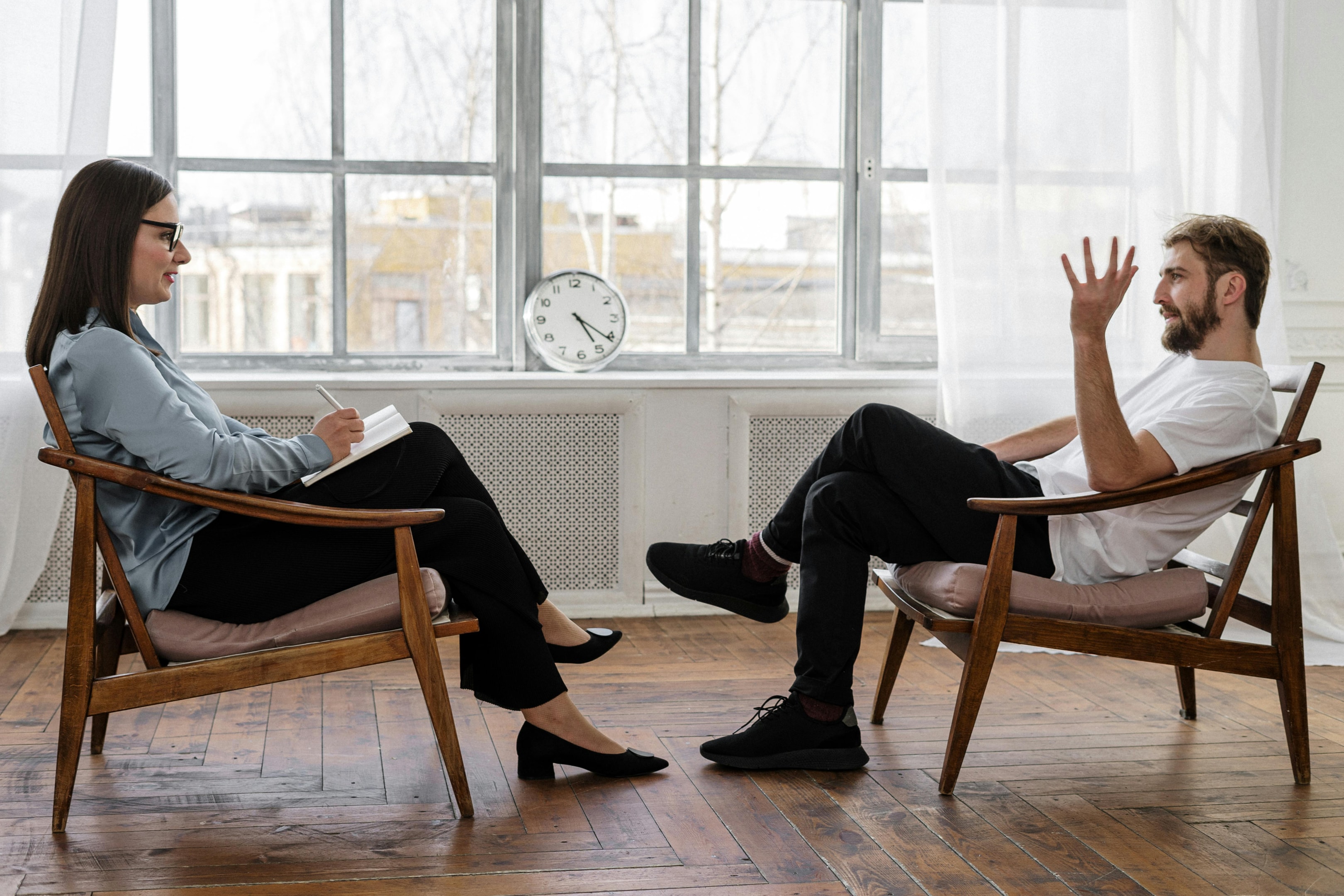

Symptoms and Warning Signs
Signs and symptoms of mental illness can vary, depending on the disorder, circumstances, and other factors.
Mental illness symptoms can affect emotions, thoughts, and behaviors.
Symptoms can appear as physical problems, such as stomach pain, back pain, headaches, or other unexplained aches and pains.
Warning signs of mental health problems include changes in mood, appetite, or sleep patterns.
Seeking Help and Diagnosis
If you have any signs or symptoms of a mental illness, see your primary care provider or a mental health professional.
A mental health diagnosis often involves a full health evaluation, including a physical exam, blood work, and/or neurological tests.
People of diverse cultures and backgrounds may express mental health conditions differently, and stigma around mental illness prevents many from seeking needed treatment.
Early intervention and treatment are essential for managing serious mental illness.
Treatment and Therapy
Mental health treatment is based on an individualized plan developed collaboratively with a mental health clinician and the individual.
Treatment may include psychotherapy (talk therapy), medication, or other therapies, often in combination.
Community-based mental health care is more accessible and acceptable than institutional care, and helps prevent human rights violations.
Community-based mental health care should be provided through a network of interrelated services that comprise a range of care options.

Neurozoom Key Points
Unique Formula: Contains 35 essential memory-boosting antioxidants, minerals, vitamins, and herbs.
Holistic Approach: Each ingredient carefully selected for maximum benefit without prescription.
Comprehensive Support: Designed to improve overall memory and concentration function.
Self-Help and Lifestyle Changes
Self-help and support are essential for coping, recovery, and well-being, and may include lifestyle changes, support groups, or exercise.
Increasing your resilience and developing coping skills can also help prevent mental illness.
Getting regular exercise and eating a healthy diet can also help reduce your risk of developing a mental illness.
Practicing good sleep habits and managing stress can also help prevent mental illness.
Supporting Loved Ones
If your loved one shows signs of mental illness, have an open and honest discussion with him or her about your concerns.
You may not be able to force someone to get professional care, but you can offer encouragement and support.
You can help your loved one find a qualified mental health professional and make an appointment.
If your loved one has done self-harm or is considering doing so, take the person to the hospital or call for emergency help.
Mental Health Promotion and Prevention
Mental health promotion and prevention interventions work by identifying and addressing individual, social, and structural determinants of mental health.
Interventions can be designed for individuals, specific groups, or whole populations, and often require action beyond the health sector.
Promoting child and adolescent mental health can be achieved through policies and laws that promote and protect mental health, and supporting caregivers to provide nurturing care.
Improving mental health requires a multisectoral approach that involves governments, communities, and individuals.
Complications and Consequences
Mental illness is a leading cause of disability.
Untreated mental illness can cause severe emotional, behavioral, and physical health problems.
Complications sometimes linked to mental illness include substance use disorders and physical health problems.
Mental illness can also increase your risk of developing other health conditions.
Access to Care and Resources
The treatment gap for mental health services is significant, with many countries allocating insufficient resources, inequitably distributing them, and using them inefficiently.
The WHO Guidance on community mental health services promotes person-centered and rights-based approaches to mental health care.
The Mental Health Services Administration provides resources and support for mental health care and services.
Access to mental health care is essential for improving mental health outcomes.
Conclusion
Mental health is a critical aspect of overall well-being that requires attention and support.
Understanding mental health conditions, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for promoting mental health and well-being.
Supporting loved ones with mental health conditions and promoting mental health in communities can help improve mental health outcomes.
Improving access to mental health care and resources is critical for addressing the mental health needs of individuals and communities.

.jpg)
No comments:
Post a Comment