Liver Health, Men's Health, Alcohol: What to Know
Do you know how alcohol can affect your liver health and overall health? As a man, it's important to know the risks of alcohol use, especially for your liver. What key factors should you consider when it comes to maintaining a healthy liver and managing your alcohol intake?
During the COVID-19 pandemic, alcohol sales went up 54%1. People drank more often, especially those feeling stressed about COVID-191. In the U.S., nearly 15 million people 12 and older had a problem with alcohol. Drinking alcohol can harm your health and well-being. It's the third-leading cause of preventable death in the U.S., with 95,000 deaths each year from alcohol-related causes.
Key Takeaways
- Alcohol consumption can have a significant impact on liver health and overall well-being, particularly for men.
- Alcohol use disorders are common, with nearly 15 million people in the U.S. affected.
- Alcohol is the third-leading preventable cause of death in the U.S., with 95,000 deaths per year.
- Understanding the risks and vulnerabilities associated with alcohol use is crucial for maintaining a healthy liver.
- Adopting healthy lifestyle habits and seeking professional help can help prevent alcohol-related liver diseases.
The Impact of Alcohol on Men's Liver Health
Drinking too much alcohol can really hurt men's liver health. It can lead to serious diseases like fatty liver, hepatitis, and cirrhosis2. In 2009, alcohol was linked to about 19,500 deaths in the U.S., making up 3.5% of all cancer deaths2. Drinking can cause different cancers, including those in the head, neck, liver, breast, and colon2. Even having one drink a day can increase a woman's chance of getting breast cancer by 5% to 15%2.
Alcohol and Liver Disease: A Serious Concern
Drinking too much can weaken the immune system, making you more likely to get infections like pneumonia2. It can also make you more prone to diseases for up to 24 hours after heavy drinking2. The liver is especially at risk, facing three major diseases from alcohol: fatty liver, hepatitis, and cirrhosis3.
Risks of Excessive Alcohol Consumption
During the COVID-19 pandemic, alcohol sales went up by 54% in the U.S., and in 2019, 15 million people over 12 needed help for alcohol use disorder3. Too much alcohol is a top cause of preventable deaths, with 95,000 people dying each year from it3. Liver disease from alcohol was a major cause of death from 2011 to 20153. Men should know the dangers of drinking too much and try to drink healthily.
"Almost all heavy drinkers develop fatty liver, the earliest stage of alcohol-related liver disease. About one-third of heavy drinkers develop alcoholic hepatitis, which can be life-threatening. 10%–20% of heavy drinkers develop cirrhosis, a serious condition that usually develops after 10 or more years of drinking."
For those without liver disease, moderate drinking means two drinks a day for men and one for women3. But even moderate drinking can be bad, as binge drinking can make the gut more open4. Drinking two drinks a day can also increase the risk of atrial fibrillation by 17%4.
Drinking too much can also affect men's sexual and reproductive health4. Almost three-quarters of men with alcohol issues face sexual problems, and just five drinks a week can lower sperm count and quality4.
It's important to know the risks of drinking too much alcohol for men's liver and overall health. By drinking healthily and getting help when needed, men can protect their liver and stay healthy234.
Learn about this product more on Official Website
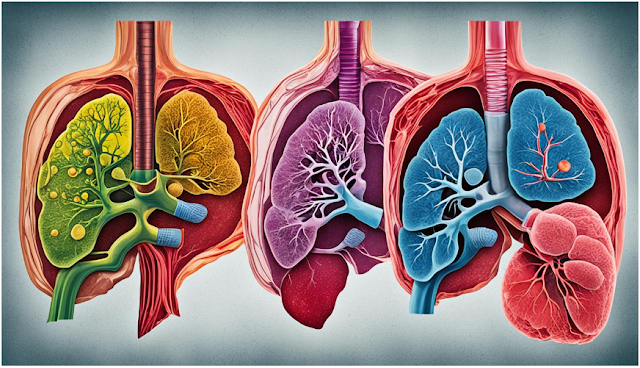
Understanding Alcohol-Related Liver Diseases
Drinking too much alcohol can harm the liver, leading to various diseases. It's important to know how these diseases progress to help prevent them.
Fatty Liver Disease: The Early Stage
Fatty liver disease, or hepatic steatosis, is often the first sign of alcohol-related liver issues. It happens in almost all heavy drinkers5. Even a few years of heavy drinking can cause it6. People with fatty liver might not feel sick, but they could have a bigger liver and feel discomfort in their upper right side.
Alcoholic Hepatitis: Inflammation and Liver Damage
Alcoholic hepatitis makes the liver inflamed and swollen, harming liver cells6. It can be mild or severe, causing symptoms like jaundice, fever, and stomach pain6. The mild form can last for years and get worse if drinking doesn't stop6. Severe cases can happen suddenly after binge drinking and are very dangerous6.
Knowing how alcohol can lead from fatty liver to hepatitis is key for men's health and preventing liver disease5. Stopping heavy drinking early and drinking healthily can reduce risks and even fix some damage.
Cirrhosis: The Severe Consequence of Alcohol Abuse
Cirrhosis is a serious condition that can last forever and often starts after years of drinking a lot7. It's a chronic liver disease that changes healthy liver tissue into scar tissue, making the liver work poorly7. This disease is a big health worry, shown by the increase in deaths from cirrhosis and liver cancer in the U.S. from 1999 to 20168.
Most people with alcoholic liver disease are between 40 and 50 years old, and men are more likely to get it7. Women can get it after drinking less alcohol than men7. The risk of getting liver disease goes up with more years of drinking and drinking more alcohol7.
As cirrhosis gets worse, people may feel tired, weak, and lose muscle, have fluid in their belly and legs, bleed from the esophagus, get confused, and act differently7. These problems can lead to liver failure and liver cancer, sometimes needing a liver transplant7.
Stopping cirrhosis before it starts is key, which means not drinking alcohol at all7. Catching it early and acting fast is important to manage it and stop it from getting worse7. Tests like CBC, liver function tests, and imaging studies help find and manage this disease7.
Even though liver disease is a big problem, there is hope8. By knowing the risks and making healthy choices, men can lower their chance of getting this serious condition and stay healthier7.
Alcohol clearly harms the liver, and cirrhosis has serious effects7. By changing how much alcohol is drunk, living a healthy lifestyle, and getting help from experts, men can protect their liver health and lower the risk of cirrhosis79.
Men and Alcohol: Increased Risks and Vulnerabilities
Men face unique challenges with alcohol, especially for their liver health. They often drink more than women, which can harm their liver10.
Gender Differences in Alcohol Metabolism
Men and women process alcohol differently due to physiological differences. Men have more of an enzyme that breaks down alcohol quickly10. This can make men more tolerant of alcohol, leading them to drink more. This increases their risk of liver diseases from alcohol.
Patterns of Drinking: Binge and Heavy Alcohol Use
Men tend to binge drink and use alcohol heavily more than women10. Binge drinking means having 5 or more drinks in 2 hours, raising blood alcohol levels and increasing risks like car crashes and memory loss10. Drinking a lot over time can cause serious health issues like liver disease and cancer10.
Men's higher binge and heavy drinking, along with how their bodies process alcohol, makes them more at risk for liver diseases1011.
It's important to address how men drink and encourage healthy habits for their liver and overall health1011.
"The higher prevalence of alcohol use and binge drinking among men, along with gender differences in alcohol metabolism, contribute to their increased risk of alcohol-related liver diseases."
Liver health, mens health, alcohol
June is Men's Health Month, a time to focus on the link between liver health and men's well-being. The liver is key for detox, metabolism, and storing nutrients. It's vital for men's health12. This month, we highlight the importance of liver health and its effect on men's lives.
Alcohol use is a big factor in liver health for men12. Men drink more alcohol than women, making them more likely to get liver diseases12. They also face a higher risk of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)12. This disease is linked to obesity, insulin resistance, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol levels12.
Alcohol's effects on the liver go beyond just alcoholic liver disease13. Drinking too much can lead to fatty liver in 90% of people. Heavy drinkers risk liver inflammation and cirrhosis13. Drinking too much can also cause memory loss, brain damage, and increase the risk of cancers, including liver cancer13.
Men can take steps to protect their liver health12. Drinking in moderation, staying at a healthy weight, getting vaccinated against hepatitis, and living a balanced life can lower liver disease risks12. By focusing on liver health and healthy habits, men can protect their overall well-being.
Reflecting on Men's Health Month, we see how vital liver health is for overall wellness. Understanding the risks and taking preventive steps helps men keep their liver healthy. This month reminds us to focus on our liver health and get the support we need for a healthier life.
Preventing Alcohol-Related Liver Diseases
Keeping your liver healthy is key for your overall health, especially for men at risk of liver diseases from alcohol. By being proactive, men can protect their liver and lower the risks from drinking too much alcohol.
Adopting Healthy Lifestyle Habits
Healthy habits are your best defense against liver diseases from alcohol. This means eating well, drinking plenty of water, and staying active. Drinking no more than 14 units a week can really help lower the risk of liver issues.1415
If you already have liver problems from alcohol, stopping or cutting back is key. This can stop early liver damage from getting worse and prevent cirrhosis14.
Seeking Professional Help and Support
Getting help for alcohol addiction and liver diseases is tough, but it's worth it. Talking to a doctor, like a liver or gut specialist, can help make a plan just for you15.
Joining support groups or counseling can also offer great help and support. By tackling the root causes and getting expert advice, you can work on making your liver healthier and avoid alcohol's bad effects.
Youtube Shorts Must Watch
"Liver health is not just about avoiding alcohol, but about adopting a holistic approach to wellness. By making positive lifestyle choices and seeking professional support, men can take control of their hepatic well-being and reduce the risks associated with alcohol-related liver diseases."
Looking after your liver is vital for your health and well-being. By choosing to drink wisely, living a balanced life, and getting help when you need it, men can prevent liver diseases from alcohol. This way, they can keep their liver healthy for the long run.
The Role of Screening and Early Detection
Regular check-ups and screenings are key for catching liver diseases early. This lets men deal with liver problems before they get worse16. Getting medical advice and doing regular liver tests helps men keep an eye on their liver health.
Screening for alcohol use is a smart move that saves money and prevents diseases16. Tools like the AUDIT-C and SASQ are great for spotting unhealthy drinking habits16.
Men should know the dangers of drinking too much alcohol1718. Regular check-ups can spot liver issues early. This means men can stop cirrhosis and liver cancer before they start.
By checking their liver health often and watching their drinking, men can keep their liver healthy161718.
"Preventive practices, such as screening and brief intervention for unhealthy alcohol use, are essential for maintaining liver health and reducing the burden of alcohol-related liver diseases in men."
Liver Cancer: A Serious Risk for Men
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a big threat to men's health. It's the most common liver cancer type. Chronic liver diseases like hepatitis B or C, alcoholic liver disease, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease raise the risk of getting liver cancer19. Hormonal and genetic factors also play a part in why men get it more often19.
Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Its Causes
Drinking too much alcohol is a big risk for HCC19. It can harm the liver, causing inflammation and scarring. This makes getting liver cancer more likely19. Drinking alcohol is also linked to more colon and rectal cancer in men19.
Smoking is another big risk for liver cancer20. People who used to smoke or smoked for over 40 years face a higher risk of HCC20. This risk is especially high in places like Asia and Africa, where liver cancer is more common20.
To lower liver cancer risk, focus on fixing liver issues and living healthily. This means drinking less alcohol, quitting smoking, eating well, and exercising regularly19. Getting checked early and catching liver cancer early can really help, especially for men19.
"Alcohol can increase the risk of cancer by acting as an irritant in the body, damaging DNA, and leading to oxidative stress in cells."19
Addressing Sexual and Reproductive Health Concerns
Too much alcohol can really hurt a man's sexual and reproductive health. Alcohol messes with testicular function and male hormone levels. This can cause erectile dysfunction and infertility21. Also, alcohol use makes men more likely to take risks in bed, like having unprotected sex or with many partners21.
Men need to deal with these sexual and reproductive health concerns to stay healthy. Impaired testosterone production, testicular atrophy, and decreased libido and sexual potency are big problems for men with severe alcoholic cirrhosis21.
Also, alcohol abuse can cause impotence, lower sperm production, and fewer sperm21. It's key to fix these issues to keep reproductive health in check and avoid more problems from alcohol.
Knowing the sexual and reproductive health concerns linked to excessive alcohol use helps men act early to protect their health. Getting help and support is key to tackling these issues and having a good relationship with alcohol.
Conclusion
The connection between liver health, men's health, and alcohol is very important. Men face a higher risk of liver diseases like alcoholic liver disease and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease22. By knowing the risks and making healthy choices, men can protect their liver and overall health.
Studies show the impact of alcohol on health worldwide23. A UK study looked at the costs of alcohol-related diseases23. In the US, research from 1990 to 2016 found the effects of alcohol on health23. A Nigerian study focused on alcohol use among outdoor drinkers23.
For healthy adults in the US, moderate drinking means not having more than one drink a day for women and not more than two for men24. Heavy drinking is having more than three drinks in one day or seven in a week for women, and four or 14 drinks for men24. Binge drinking is when blood alcohol levels hit 0.08%, which is four or five drinks in two hours for women and men, respectively24.
Learn about this product more on Official Website
FAQ
What is the connection between liver health, men's health, and alcohol consumption?
Drinking too much alcohol can harm the liver and lead to diseases like fatty liver, hepatitis, and cirrhosis. Men often drink more and face higher rates of alcohol-related health issues and deaths than women.
What are the main types of alcohol-related liver diseases?
There are three main liver diseases linked to alcohol: fatty liver, hepatitis, and cirrhosis. Fatty liver is the first stage, seen in most heavy drinkers. Hepatitis and cirrhosis are more serious and can be deadly.
Why are men more prone to alcohol-related liver diseases?
Men tend to drink more and binge drink more often than women. They also metabolize alcohol differently, making them more at risk for liver diseases.
How can men prevent and manage alcohol-related liver diseases?
Men can cut down on drinking, eat well, drink plenty of water, exercise, and get help if needed. Regular doctor visits and screenings help catch and manage liver diseases early.
What is the link between liver cancer and alcohol consumption in men?
Long-term liver diseases from too much alcohol raise the risk of liver cancer. Men get liver cancer more often, possibly due to hormones and genes.
How does alcohol use affect men's sexual and reproductive health?
Too much alcohol can harm testicular function and lower male hormone levels. This can cause erectile dysfunction and infertility. It also makes risky sexual behavior more likely, leading to negative outcomes.
Source Links
- https://www.cdc.gov/alcohol/fact-sheets/mens-health.htm - Excessive Alcohol Use and Risks to Men's Health
- https://www.niaaa.nih.gov/alcohols-effects-health/alcohols-effects-body - Alcohol's Effects on the Body
- https://www.mayoclinichealthsystem.org/hometown-health/speaking-of-health/effects-of-alcohol-on-your-health-and-liver - Effects of alcohol on health and liver
- https://www.menshealth.com/health/a19541206/your-body-on-booze/ - This Is Your Body on Booze
- https://www.uofmhealth.org/conditions-treatments/digestive-and-liver-health/alcohol-related-liver-disease - Alcohol Related Liver Disease | University of Michigan Health
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK546632/ - Alcoholic Liver Disease - StatPearls
- https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/diseases-conditions/alcoholic-liver-disease - Alcoholic liver disease
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6776700/ - Alcohol consumption and risk of liver cirrhosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/alcoholinduced-liver-disease - Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease
- https://www.niaaa.nih.gov/health-professionals-communities/core-resource-on-alcohol/basics-defining-how-much-alcohol-too-much - The Basics: Defining How Much Alcohol is Too Much
- https://www.niaaa.nih.gov/health-professionals-communities/core-resource-on-alcohol/medical-complications-common-alcohol-related-concerns - Medical Complications: Common Alcohol-Related Concerns
- https://cpmiclinical.com/mens-guide-to-a-healthy-liver/ - Men's Guide to a Healthy Liver - Clinical Pharmacology of Miami
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/alcohol-good-or-bad - Alcohol and Health
- https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/alcohol-related-liver-disease-arld/ - Alcohol-related liver disease
- https://www.nhsinform.scot/illnesses-and-conditions/stomach-liver-and-gastrointestinal-tract/alcohol-related-liver-disease/ - Alcohol-related liver disease
- https://www.niaaa.nih.gov/health-professionals-communities/core-resource-on-alcohol/screen-and-assess-use-quick-effective-methods - Screen and Assess: Use Quick, Effective Methods
- https://www.gwhospital.com/about/blog/9-essential-screenings-men - 9 Essential Screenings for Men
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6883141/ - Prevention, screening, and treatment for heavy drinking and alcohol use disorder
- https://www.cancer.org/cancer/risk-prevention/diet-physical-activity/alcohol-use-and-cancer.html - Alcohol Use and Cancer | Health Effects
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9722635/ - A prospective cohort study of cigarette smoking, alcohol drinking and liver cancer incidence in Chinese men
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6761906/ - Alcohol’s Effects on Male Reproduction
- https://health.clevelandclinic.org/millennials-and-alcohol-more-young-people-are-drinking-to-the-point-of-liver-damage - Millennials and Alcohol: More Young People are Drinking to the Point of Liver Damage
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7005647/ - Public health policies and alcohol-related liver disease
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/in-depth/alcohol/art-20044551 - Alcohol in moderation: How many drinks is that?





.jpg)
No comments:
Post a Comment